Blockchain: digital information “the block” stored in public database “the chain”.
- A blockchain network is a combination of computers linked to each other instead of a central server, meaning the whole network is decentralized.
- A blockchain is a record of transaction. It’s at the heart of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum and can be used to document financial transactions, the movement of goods or services and or exchanges in information
Let’s dive into it
A blockchain is just a database. Very simply, it’s a growing set of records bunched together into “blocks” which are linked together using cryptography.
How does blockchain keep those records?
In a distributed ledger, a record of every transaction is held in many places at the same time. Every time something in the blockchain is changed, everyone in the network is notified about and has to agree on changes.
These consensus protocols make a blockchain very difficult to hack into and change records as it would require someone to change every single record at the exact same time.
What are the peculiarities of the blockchain?
One of the first peculiarities with these databases is that blockchains are append-only. That means that you can only add information – you can’t just click on a cell and delete information that you’ve already added, or change it in any way.
The second is that each entry (called a block) in the database is cryptographically linked to the last entry. In plain English, each new entry must contain a sort of digital fingerprint (hash) of the last one.
And that’s it! Since each fingerprint points back to the last one, you end up with a chain of blocks. Or – as we use to call it – a blockchain.
A blockchain is immutable: if you change a block, it changes the fingerprint. And since that fingerprint is included in the next block, the next block is changed too. You end up with a domino effect where any change becomes evident. You can’t alter any information without everyone noticing.
Let’s illustrate it 🙂
How a blockchain transaction works?
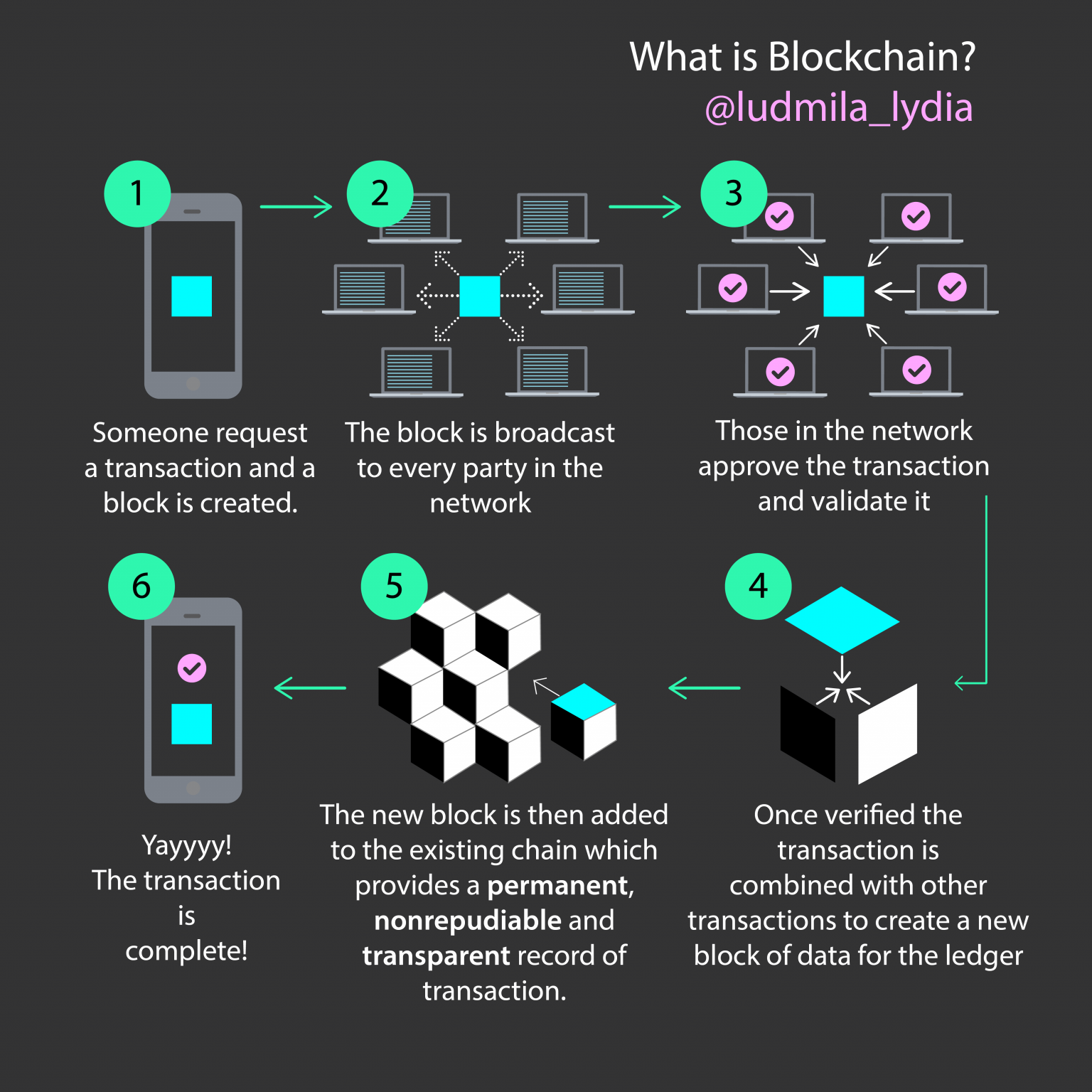
How does the whole process work?
- A transaction is requested and a block that represents that transaction is created.
- The block is sent to every participant “node” in the network.
- Nodes – participants – validate the transaction
- The block is added to the existing blockchain
- The transaction is finally complete
Each of these blocks of data (i.e. block) are secured and bound to each other using cryptographic principles (i.e. chain).
Any new record or transaction within the blockchain implies the building of a new block, and the whole process will repeat.
Each record is then proven and digitally signed to ensure its genuineness.
Before this block is added to the network, it should be verified by the majority of nodes in the system.
Why is everyone so excited about blockchain?
There are a number of key factors that make blockchain so exciting.
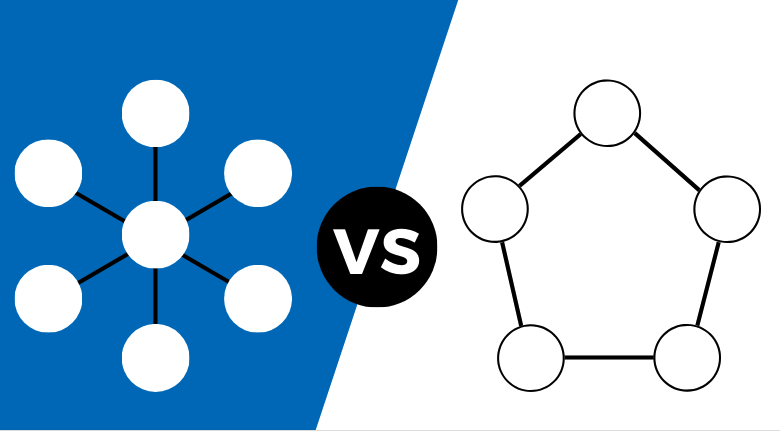
It’s decentralized.
The internet today is mostly centralized. What does that mean? The vast majority of the services and sites you visit store and keep their data in a database. Your bank, Netflix, Google… they all operate a centralized system.
The blockchain meanwhile, is a decentralized system. That means that the data lives on the network, instead of in one place.
In the present centralized system, there are a number of challenges.
- Security – If these centralized databases get hacked into, they can expose all the data at once. We’ve seen that happen more and more recently.
- Cost – Building centralized systems is often expensive as a company needs to provide all the digital capacity to make a system run smoothly.
- Your data – In these centralized systems, your data is not your own, and is often monetized by the networks you give that data too.
- Transparency – How information gets used, by whom and for what is a bit of a grey area today. The decentralized internet can change that!
It’s a trustless system
Today when we buy things online, there are a number of actors or points we have to trust. Whether it be a seller, a payment system, a bank or even a website. A blockchain doesn’t require so much trust, allowing anyone to exchange goods or services without a third party.
No more middlemen
Many of today’s networks are controlle by middlemen or agencies that often charge for the flow of information. In a blockchain, there is no such control which can lead to lower cots and speedier transactions.
Transparency
In a public blockchain like Bitcoin (there are private blockchains) anyone can see transactions, making it easier to track the flow of goods or services.
No one is in control
Because blockchain is a decentralized system, it means no one person or group can control the system. Things can only change via consensus.
That’s it guys, I hope this little introduction has been useful. You can see here that blockchain is way more than Bitcoin.
Blockchain started with Bitcoin but there is no limits to where this technology will go in the future. That’s just the beginning.
That’s it guys. Please leave a comment down below for any question you have about this article and I’ll be answering! Remember, we are all here to learn and there are no stupid questions
Thank you !