After achieving widespread adoption throughout the Web3 community, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are making their way into the mainstream, with spotlights in major media outlets and a series of high-profile athletes and public figures launching their own collections. As a result, NFTs have become one of the most publicly prominent applications of blockchain technology.
The next step in the evolution of NFTs is just getting started. Dynamic NFTs (dNFTs) are expanding the design space that NFTs are able to address through their ability to adapt and change in response to external events and data. In this article, we cover what NFTs are and how dNFTs are taking them to the next level, current and potential dNFT use cases, and how decentralized oracles like Chainlink can be leveraged by those looking to build dNFTs to give them access to trust-minimized off-chain data and computation.
Table of Contents:
- Understanding NFTs
- Going Beyond Static NFTs With Dynamic NFTs (dNFTs)
- What is a dynamic NFT, or dNFT?
- What dynamic NFTs are not
- Potential Use Cases
- Dynamic NFT Examples
- Are dynamic NFTs more valuable than static NFTs?
- Dynamic NFTs: the future of the NFT space?
- Oracles and dNFTs
Understanding NFTs
In a nutshell, NFTs are unique digital objects that exist on a blockchain. Every NFT can be differentiated from another through a 1-of-1 tokenID and its unique contract address. From there, metadata such as images, video files, or other data can be attached, meaning that it’s possible to own a token that represents a unique digital object.
The most common NFT use case is currently digital art; an artist mints a token representing a digital artwork and a collector can purchase that token, marking their ownership. Once NFTs are minted, their tokenIDs don’t change. Keep in mind that ascribing metadata, which incorporates an NFT’s description, image, and more is completely optional. In its most bare-bones form, an NFT is simply a transferable token that has a unique tokenID.
This static NFT model provides a host of benefits for digital artists around the world. Beforehand, digital artists were unable to stop, or even track, unauthorized distribution of their original artwork, because there was no means by which to distinguish the difference between any two files and therefore no single authentic file that could be owned. For the first time in the history of the Internet, creators can sell digital art to their fans by giving them verifiable ownership, while fans can prove that they own an original artwork even if the underlying image is copied.
Going Beyond Static NFTs With Dynamic NFTs (dNFTs)
Static NFTs are currently the most common type of NFT, used for the most part by NFT art projects and play-to-earn game projects and as digital collectibles. Beyond these use cases, they also offer a unique value proposition for digitizing items in the real world, such as real estate deeds, patents, and other unique identifiers.
However, this model is limited by the permanence of static NFTs, because the metadata attached to them is fixed once they’re minted on a blockchain. Use cases such as tokenizing real-world assets, building progression-based video games, or creating blockchain-based fantasy sports leagues often require data to be updated. dNFTs offer a best-of-both-worlds approach, with NFTs retaining their unique identifiers while able to update aspects of their metadata.
What is a dynamic NFT, or dNFT?
Dynamic NFTs, as the name suggests, refers to a type of NFTs that change according to certain circumstances that trigger their smart contracts.
They are also often referred to as “Living NFTs”, and can have their characteristics change because of a special event or a real-world occurrence, and also see their value and demand shift.
Put simply, a dynamic NFT is an NFT that can change based on external conditions. Change in a dNFT often refers to changes in the NFT’s metadata triggered by a smart contract. This is done by encoding automatic changes within the dNFT smart contract, which provides instructions to the underlying NFT regarding when and how its metadata should change.
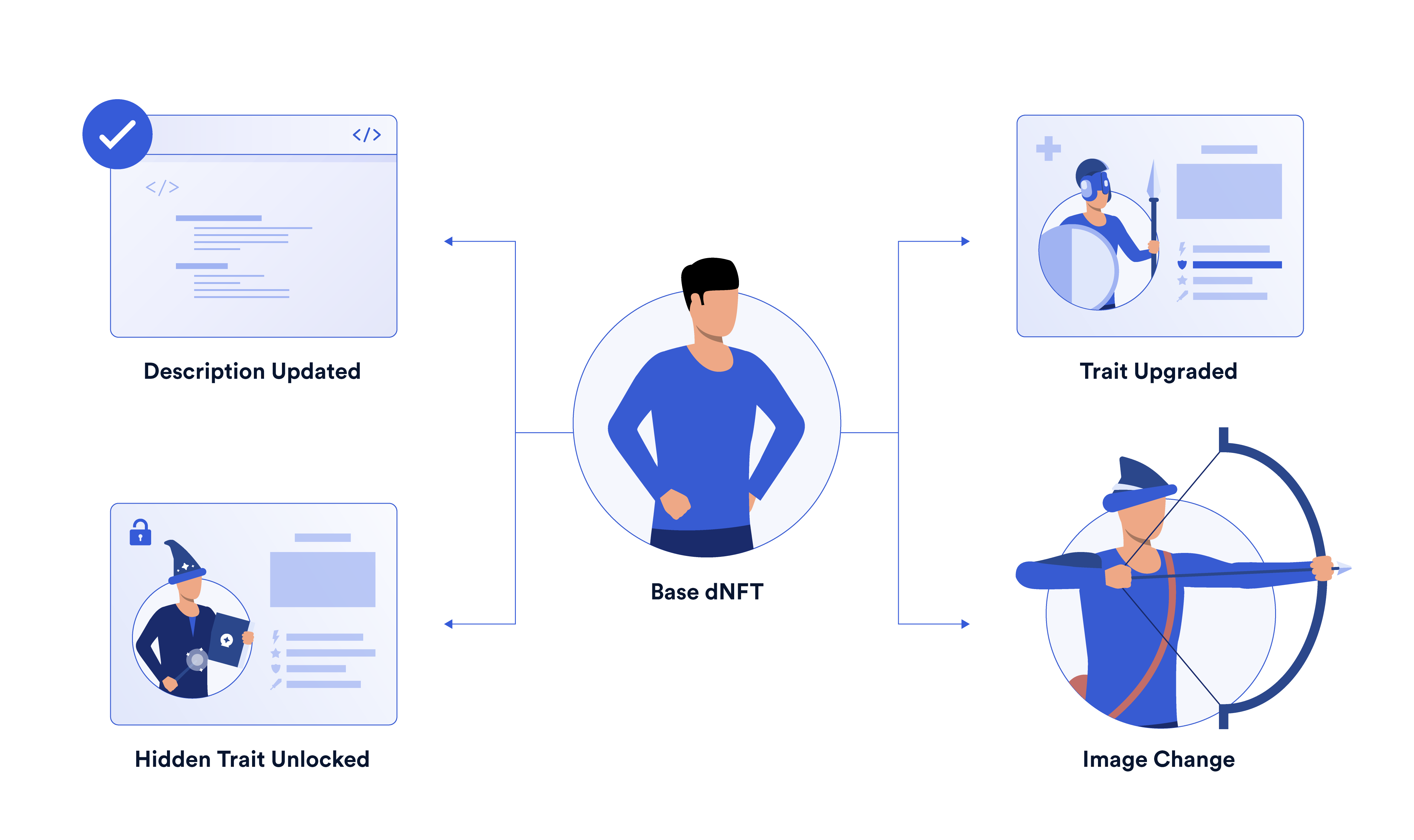
Dynamic elements besides metadata changes can also exist. For example, dNFTs can be minted based on certain conditions, such as when a hidden spot is found in an augmented reality application. Dynamic NFTs can also house “hidden traits” manifested through user interactions instead of within the metadata. As fully unique and customizable tokens, NFTs can be programmed in an infinite number of ways. However, most dynamic NFTs must implement some form of metadata change in order for non-technical users to “see” the changes.
Technically speaking, dynamic NFTs are actually semi-fungible tokens – or ERC-1155 tokens, unlike traditional static ERC-721 NFTs.
They have, according to the official Ethereum website, the same features as the improved ERC-20 and ERC-721 token standards. In other words, the best of both worlds.
Once the dNFT receives the instruction in the smart contract and confirms it, it will display the predetermined change in the token’s metadata.
What dynamic NFTs are not
For an NFT to be dynamic, it doesn’t have to be a moving picture, like a GIF or video. Sure, GIFs and videos can be NFTs, but these would also be static NFTs.
To be dynamic, an NFT needs to have its state altering from one point to another. This change takes place in the NFT’s metadata and can also be shown in how it looks.
Potential Use Cases
NFT metadata is where the token’s name is specified, traits are assigned, and file links are placed. While the tokenID provides a permanent identifier for verifiable ownership, the metadata is the essence of the NFT—housing the elements that make it useful.
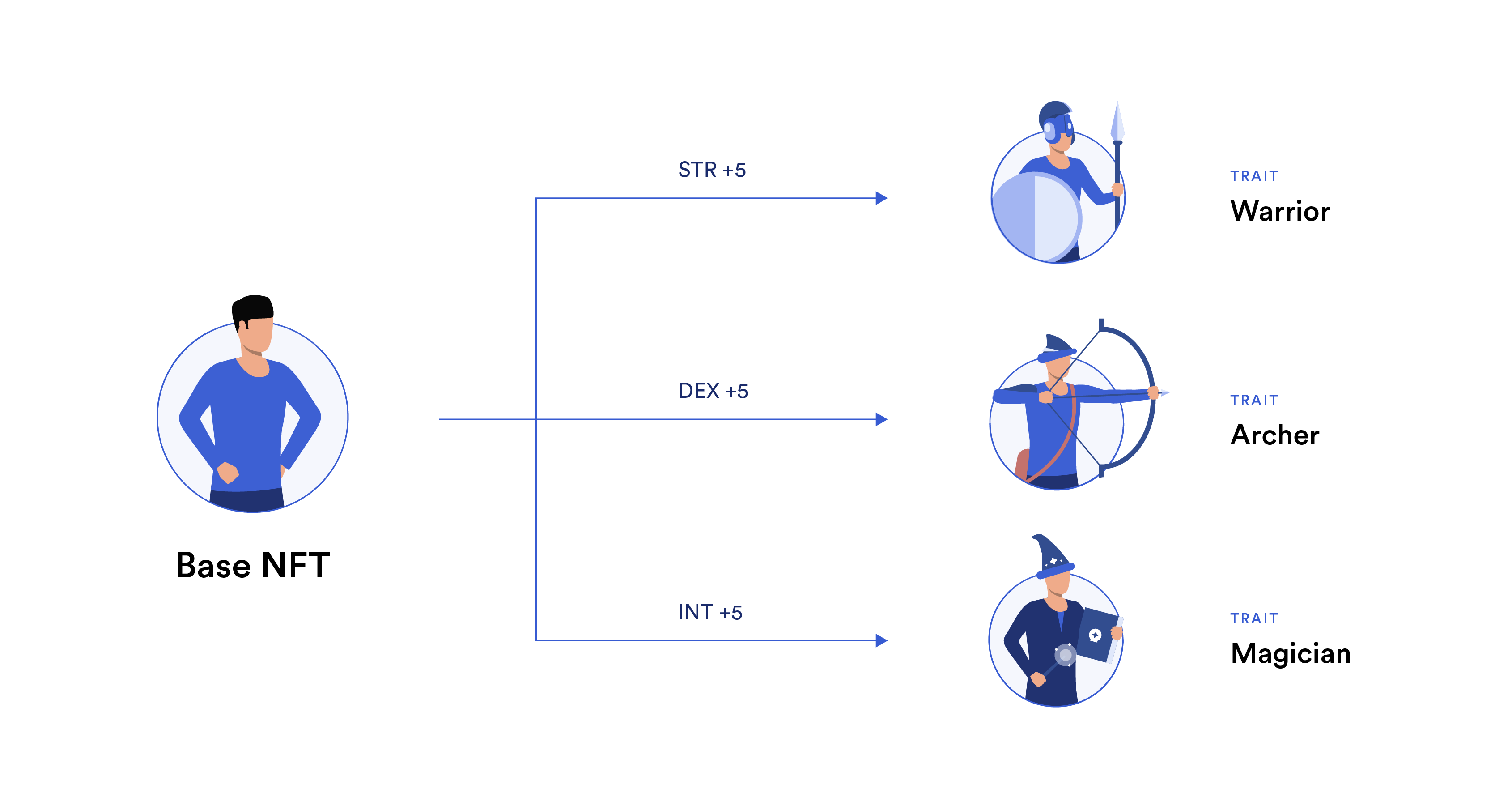
Generative NFT art projects often have a variety of traits, with some rarer than others. These traits are placed within an NFT’s metadata alongside an IPFS link to an image or video that corresponds to the NFT’s traits. In a dNFT, these traits change based on external conditions.
This functionality can be useful for character progression—a core tenet of many different game models—in blockchain games. When first starting a game with a playable dNFT character, the dNFT has base stats reflected in its metadata. As the player continues leveling up, the metadata in the dNFT changes to reflect the character’s growth.
Another case where metadata changes are useful is in the tokenization of real-world assets, where a host of changing metrics are often required. For example, a dNFT representing a property could reflect its maintenance history, age, market value, and more. Tokenizing these changing assets therefore requires NFTs which have the ability to update with changing metadata.

These are just a few hypothetical use cases for dNFTs. In reality, changes to a dNFT’s metadata can be triggered by any number of off-chain or on-chain events, speaking to the limitless potential of dNFTs have for expanding the NFT design space.
While the current Web3 ecosystem mostly consists of static NFTs, a few standout projects have already kickstarted dNFT innovation.
Dynamic NFT Examples
Dynamic NFTs can be applied in various ways across different Web3 areas. Get to know below some of the best examples of dNFTs that are already trending in sports, gaming, collectibles, fundraising and art.
dNFTs in sports: The Association NFTs
One of the most practical ways to use dynamic NFTs is to tie them to real-world happenings, such as those that take place in sports. Sports NFTs are not new to the industry, and they have been extremely well received by the community since the NBA Top Shot collection in 2021.
Some collections of dynamic NFTs in the sports world are changing their tokens’ properties according to how players represented on NFTs do in matches.
In April 2022, the NBA launched a new collection of dynamic NFTs built on Ethereum called The Association.

“A week after launch, the Association generated a trading volume of over $13 million and was the 14th most traded collection. (…) These numbers are much higher when compared to NBA Top Shot at the same time after launch. For reference, it took NBA Top Shot four months to reach $1 million in sales volume and six months to surpass a volume of $13 million.”
Boris Rebo at DappRadar Report
These dNFTs change in appearance (and in value) based on player and team on-court performance. While NBA’s previous collection took the NFT discussion to TV shows and dinner parties around the world, The Association still has more to conquer – and perhaps a lot more to add to the community.
dNFTs in gaming: Otherdeeds land NFTs
Another popular way to use NFTs is on Metaverse virtual worlds and blockchain games, such as the Otherside Metaverse.
Idealized by the same creators of the Bored Ape Yacht Club NFT collection, this virtual world contains 100,000 land NFTs called Otherdeeds. And they are, you guessed correctly, dynamic NFTs.
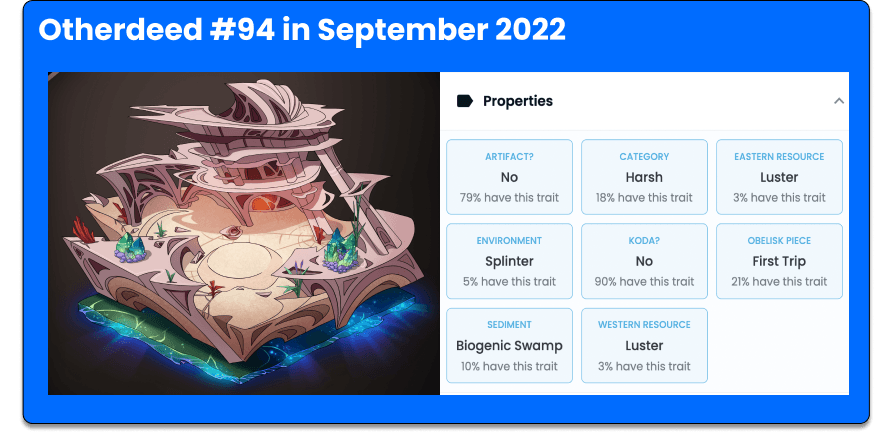
This means that, once you own this land and play on it, you can change its characteristics in the smart contract itself.
The more you develop your in-game land, the more valuable your Otherdeed becomes – a beautiful example of dynamic NFT applied to gameplay.
Artistic dNFTs: JacksonNFT
Very popular but until then a bit stagnant, artistic NFTs are also starting to develop projects with this innovative technology. This is the case with the JacksonNFT collection.
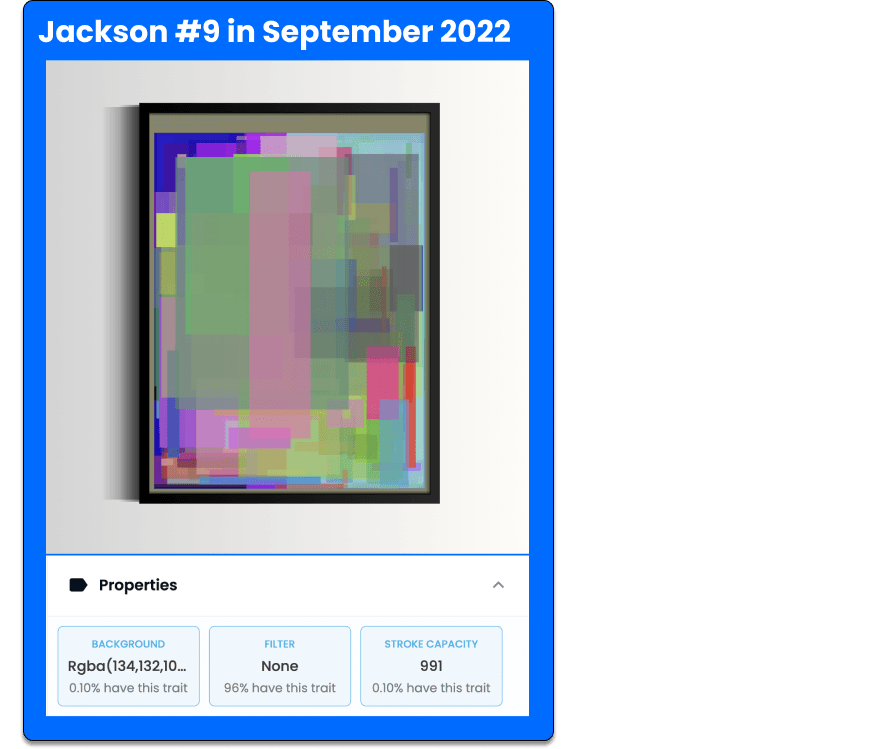
“The JacksonNFT is unique in that every time someone mints a new one, they add a new brush stroke to all the other ones. By the time all 1,000 tokens are minted, it will represent a genuinely collaborative work of art.”
Lawrence Rogers, the artist behind JacksonNFT
The collection sold out in minutes after its launch in July 2022 and could be one of the first to lead the dynamic and generative NFTs trend.
LaMelo Ball NFTs
In the past year, professional sports players such as LaMelo Ball—a rising star in the NBA—have created pioneering dNFTs that leverage Chainlink Sports Data Feeds to redefine player-fan relationships.
There are currently eight different LaMelo Ball NFTs, with each NFT recording a different set of LaMelo’s player statistics, from rebounds and assists to points scored. NFT holders can receive special access to raffles and other NFT-specific perks based on LaMelo’s ongoing performance.
One of these eight NFTs, the Gold Evolve NFT, came with a unique promise: If LaMelo Ball won Rookie of the Year for the 2021 NBA season, the dNFT itself would evolve to reflect a new image. LaMelo won the award and the dNFT evolved.
LaMelo Ball NFTs are a prime example of dNFTs that change continuously based on external data. In this case, LaMelo’s player statistics are constantly updated on-chain within the dNFT and can trigger display upgrades, rewards, and more.
Regenerative Resources Short Film NFTs
Regenerative Resources (RRC) is an ecosystem services company that aims to transform degraded land into productive seawater landscapes.
RRC announced that it will launch five dynamic Short Film dNFTs designed by prominent artists, the funds from which will be used to seed and grow 100 million mangroves across RRC’s current projects.
Each Short Film dNFT will initially have only a single frame. However, every time a dNFT is bought or resold, more frames will be released in a continuous process until the holder can view the entire short film.
Passports with Dynamic NFT elements
Governments can theoretically issue passports in the form of dynamic NFTs that update information as a person travels. There will be no need for a stamp or additional paperwork since the information is stored in the blockchain. It will also reduce the possibility of fraud as the blockchain makes them immutable and verifiable.
Are dynamic NFTs more valuable than static NFTs?
That depends on inumerous factors. The value of an NFT changes according to the public interest in the NFT market, the project’s reputation, the artist and team behind it, and so on and so on.
With dynamic NFTs, however, there’s an extra factor added to it, and that is the ability to change itself – which can be good or bad, depending on how the change is perceived.
For instance, if a sports dNFT gets more valuable because the player is doing great this season, that’s great! But if the player represented on your dNFT doesn’t stand out, your asset may have its value stagnant.
On dynamic NFTs related to gaming, you can also see your token value increase if it becomes more appealing to the community.
Time alone will tell whether or not dynamic NFTs turn out to be more valuable than static NFTs.
Dynamic NFTs: the future of the NFT space?
The NFT space is fairly young and still has much ground to win. As you can read on the latest DappRadar’s Industry Reports, NFT dapps are some of the best-performing during this crypto winter of 2022.
As NFTs evolve and use cases emerge that are specific and unique from the speculation that has dominated the market in 2021, there is no question that NFTs will play a significant role in the next bull run.
Sara Gherghellas, Blockchain Analyst at DappRadar
While some of Web3’s biggest brands are betting on collections of dynamic NFTs, we see a confident shift in industry trends – one that’s certainly worth following closely.
Where can I buy a dynamic NFT?
Just like with regular static NFTs, you can buy a dynamic NFT on marketplaces, such as OpenSea, or on the projects’ official websites.
The process is exactly the same as purchasing a static NFT. You will be able to place a bid in an auction, for example, and pay a certain amount in cryptocurrencies. After the purchase is confirmed, you will be able to find the new NFT in your wallet.
Oracles and dNFTs
How Chainlink Supports dNFTs
An often overlooked component of dNFT design is how to reliably source the information and functionality needed to build a secure, fair, and automated dNFT process.
As mentioned above, dynamic NFT metadata changes can be triggered in numerous ways based on external conditions. These conditions can exist both on and off-chain. However, blockchains are inherently unable to access off-chain data and computation.
Chainlink enables these limitations to be overcome by providing various off-chain data and computation services that can be used as inputs to trigger dNFT updates. As the dNFT ecosystem expands and NFTs become more heavily integrated with the real world, Chainlink acts as a bridge between the two disconnected worlds, enabling automated, decentralized, and engaging dNFT processes to be built.
Chainlink Data Feeds and Any API
Chainlink Data Feeds is an off-chain data delivery service that can securely deliver sports results, weather readings, or any other kind of data to be used to update a dNFT. For data offerings that are unique to a project, Chainlink also enables seamless connections between any API and an NFT smart contract through Chainlink Any API.
This service is mission-critical for use cases like LaMelo Ball dNFTs, which require on-chain sports data to trigger metadata changes. However, this is one of a limitless number of potential uses. As the most widely used decentralized oracle network, Chainlink is positioned to provide off-chain data to any dNFT that uses real-world data.
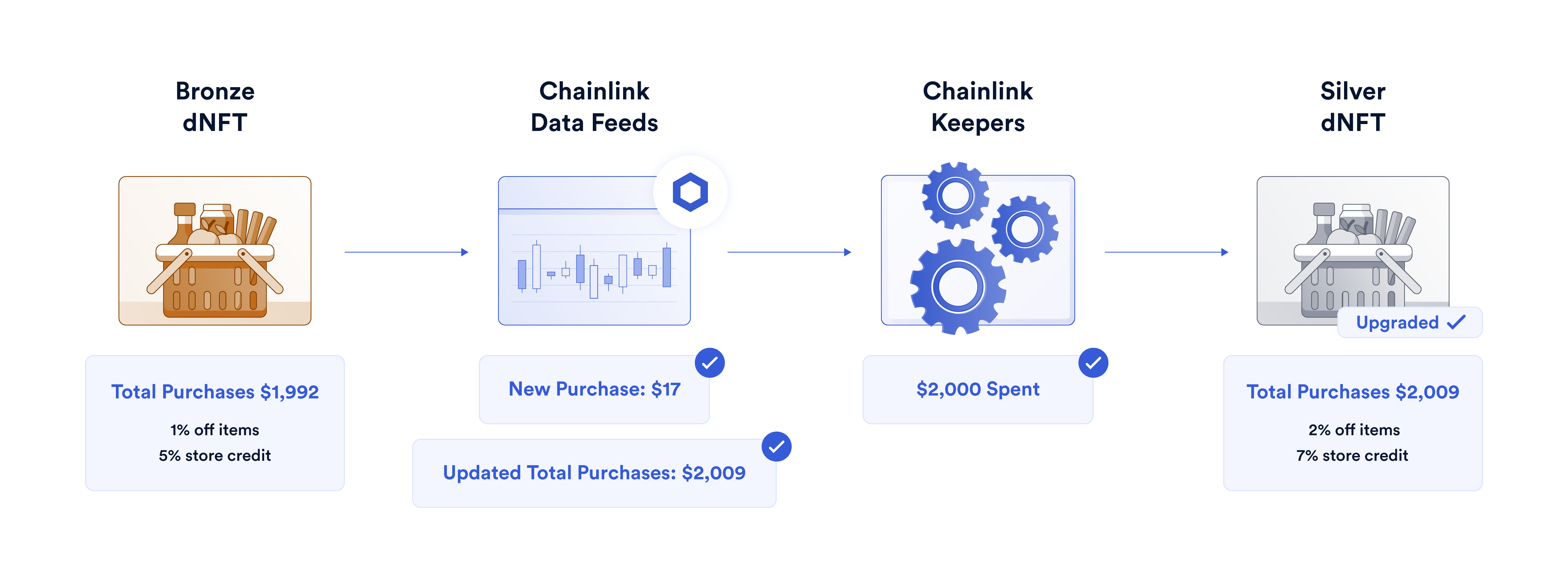
Chainlink Automation
Chainlink Automation is a secure smart contract automation service that can be used to trigger dynamic NFT changes when predefined conditions are met; to trigger visual changes in La Melo Ball NFTs when he reaches a certain stat threshold, such as 1000 points scored, for example.
Chainlink Automation provides an easy path to building truly autonomous and decentralized NFT processes and help ensure that user-owned dNFTs will work exactly as detailed. Combined with Chainlink Data Feeds and Any API, Chainlink Automation can enable the development of automated and engaging shopping rewards dNFT programs, eco-friendly behavioral tracking through dNFTs, and more.
Chainlink Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Chainlink VRF is a verifiable RNG that can be used to jumpstart dynamic changes in a dNFT—a functionality that’s particularly relevant for GameFi projects. Randomness is integral to the vast majority of video games, used to determine the success rate of attacks, decide what items come out of a loot box, or even do something as granular as decide what color a character’s shirt will be after using a cloth dye, for example.
Because play-to-earn games carry real value, it’s absolutely crucial that the RNG mechanism they use is transparent and tamper-proof.
Bringing NFTs to Life
Dynamic NFTs are living tokens that can change and evolve over time. The terminology in this space is evolving as well, traditional NFTs are increasingly being referred to as “static NFTs” because they remain the same.
Dynamic NFTs are an important innovation. They enable an extensive range of use cases and enhance the capabilities of the Web3 environment. Dynamic NFTs will be an essential tool that brings the natural and digital worlds closer.